两个线程中有一个没有经过while()条件判断,就直接进入while循环体了,导致多输出一次数据?
0
[已解决问题]
解决于 2017-11-25 13:03


主要实现功能是:使用两个线程循环打印AB。
出现的问题:当调用PrintB中的run()时,通过Debug模式调试发现,是先进入循环体,再进行的条件判断,导致最后的结果就会多输出一次数据。
源码如下:
1 /** 2 * 共享资源:打印机 3 * @author Tangxkun 4 * 5 */ 6 public class Printer { 7 8 //最大打印次数 9 private final int MAX_COUNT = 7; 10 //false表示该打印机未打印A,true表示该打印机正在打印A 11 private boolean printingA = false; 12 private int count = 0; 13 14 public synchronized void printA(){ 15 System.out.print(count++); 16 printingA = true; 17 System.out.print("A-"); 18 notifyAll(); 19 } 20 public synchronized void printB(){ 21 System.out.print(count++); 22 printingA = false; 23 System.out.print("B-"); 24 notifyAll(); 25 } 26 public synchronized void aWaiting() throws InterruptedException{ 27 while(printingA == true){ 28 wait(); 29 } 30 } 31 public synchronized void bWaiting() throws InterruptedException{ 32 while(printingA == false){ 33 wait(); 34 } 35 } 36 37 public int getCount() { 38 return count; 39 } 40 public void setCount(int count) { 41 this.count = count; 42 } 43 public int getMAX_COUNT() { 44 return MAX_COUNT; 45 } 46 }
/** * 打印A的线程 * @author Tangxkun * */ public class PrintA implements Runnable{ private Printer printer; public PrintA(Printer printer) { super(); this.printer = printer; } @Override public void run() { while(printer.getCount() < printer.getMAX_COUNT()){ printer.printA(); try { printer.aWaiting(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
/** * 打印B的线程 * @author Tangxkun * */ public class PrintB implements Runnable{ private Printer printer; public PrintB(Printer printer) { super(); this.printer = printer; } @Override public void run() { while(printer.getCount() < printer.getMAX_COUNT()){ try { printer.bWaiting(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } printer.printB(); } } }
/** * 测试代码 * @author Tangxkun * */ public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Printer printer = new Printer(); PrintA printA = new PrintA(printer); PrintB printB = new PrintB(printer); Thread threadA = new Thread(printA,"A"); Thread threadB = new Thread(printB, "B"); threadA.start(); threadB.start(); } }
当设置MAX_COUNT=5时,输出结果为: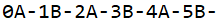
当设置MAX_COUNT=6时,输出结果为:
当设置MAX_COUNT=7时,输出结果为: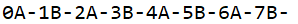
烧脑了半天还是没有找出端倪,所以来请教一下各位大神!
最佳答案
0
原因终于找到了,是自己没有理解清楚线程挂起的概念。第一次执行线程B的时候,会while条件判断进入,然后挂起,并没有执行printer.printB(),当线程A唤醒线程B时,线程B从挂起时刻的代码处继续往后执行(执行printer.printB(),完成之前被挂起的任务),而不是重新开始执行run(),也就是说,不会再进行while条件判断,最后再次进入while循环。非常感谢Daniel Cai的启发。
其他回答(1)
0
count加个volatile修饰看看。
还是和之前一样。。。
@Gient: 以你倒数第二个周期时刻为例,这个时候PrintB已经已经执行了printer.printB();然后循环检查数量限制,发现当前count(4)小于5(以最大5次为例),然后就进入等待,之后A再次启动后b又可以继续运行了致使你多了一次。
ps:为毛写这么纠结的玩意?用个CountdownLatch不就可以了么?












