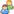来探讨远古编程时代的servlet dao层(jdbc)一个问题

如下是一个通过id获取对象的方法,咋一看没有问题,但是
String sql = "select * from cardinfo where card_id="+id;
这样拼id的写法,当调用两次dao.getCardById(不同的id) 的时候,返回的对象是同一个,并且是第一个。
这是为什么呢?
//通过CardID查询Card
public CardInfo getCardById(String id) throws SQLException {
Connection conn=null;
PreparedStatement ps=null;
ResultSet rs = null;
CardInfo card = new CardInfo();
String sql = "select * from cardinfo where card_id="+id;
System.out.println(sql);
try {
conn= DBhelper.getConnection();
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
rs = ps.executeQuery();
while(rs.next()){
card.setCardId(rs.getString(1));
card.setCurType(rs.getString(2));
card.setSavingType(rs.getBoolean(3));
card.setMoney(rs.getString(4));
card.setPrestore(rs.getInt(5));
card.setPassword(rs.getString(6));
card.setOpenDate(rs.getTimestamp(7));
card.setReportLoss(rs.getBoolean(8));
card.setCustomerId(rs.getInt(9));
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
DBhelper.closeConnection(rs,ps,conn);
}
System.out.println(card.toString());
return card;
}
正确写法为:
- 使用 ps.setString(1,id); 设置sql
//通过CardID查询Card
public CardInfo getCardById(String id) throws SQLException {
Connection conn=null;
PreparedStatement ps=null;
ResultSet rs = null;
CardInfo card = new CardInfo();
String sql = "select * from cardinfo where card_id=?";
System.out.println(sql);
try {
conn= DBhelper.getConnection();
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1,id);
rs = ps.executeQuery();
while(rs.next()){
card.setCardId(rs.getString(1));
card.setCurType(rs.getString(2));
card.setSavingType(rs.getBoolean(3));
card.setMoney(rs.getString(4));
card.setPrestore(rs.getInt(5));
card.setPassword(rs.getString(6));
card.setOpenDate(rs.getTimestamp(7));
card.setReportLoss(rs.getBoolean(8));
card.setCustomerId(rs.getInt(9));
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
DBhelper.closeConnection(rs,ps,conn);
}
System.out.println(card.toString());
return card;
}
另外,我验证过,DBhelper.closeConnection(rs,ps,conn);是生效的。
debug看了吗,第二次sql变没变
变了的
@练涛: 
我的没问题,还有你数据表里面的列名分别叫”1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9“吗?
@练涛:
public class JdbcDao {
public Index selectNameById(int id){
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Connection conn=null;
PreparedStatement ps=null;
ResultSet rs = null;
Index sms = new Index();
String sql = "select * from user where id=" + id;
System.out.println(sql);
try {
conn= DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/blu?characterEncoding=UTF-8"," "," ");
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
rs = ps.executeQuery();
while(rs.next()){
sms.setUsername(rs.getString("username"));
sms.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
ConnectUtil.closeAll(conn,ps,rs);
}
System.out.println(sms.toString());
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
JdbcDao jdbcDao = new JdbcDao();
jdbcDao.selectNameById(1);
jdbcDao.selectNameById(2);
}
}
@练涛: 这样写一般是没有问题的,并且效率还高,只是不能防止sql注入
@無腳鳥: 我就迷茫了。
@無腳鳥: rs.getString()是有两种写法的。我比较懒的写字段名,就用的另一种。
@练涛: 受教了,但是我仍然看不出你的问题在哪,我测试了没有关流,结果依然正常。
@無腳鳥: 辛苦辛苦。![]()
先不管了。
@练涛: 一起学习