线程 synchronized 问题

package com.test;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class AutomicityTest implements Runnable {
private int i = 0;
public int getValue() {
return i;
}
public synchronized void evenIncrement() {
i+=2;
/*i++;
i++;*/
}
@Override
public void run() {
while(true) {
evenIncrement();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
AutomicityTest automicityTest = new AutomicityTest();
exec.execute(automicityTest);
while (true) {
int value = automicityTest.getValue();
if(value%2 != 0) {
System.out.println(value);
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
}
evenIncrement() 这个方法的 i+=2; 程序不会停, 变成 i++ ;i++;程序就停了
大哥大姐们看一下

首先你要理解红框处代码的意思:
if( value%2 != 0 ) {}
value是奇数才会进入if代码块,而 i 默认值为0,是个偶数,i+=2肯定一直都是偶数,所以就死循环了;i++,++i是加1操作,为奇数,执行 System.exit(0); 退出虚拟机。
synchronized 不是表示这个方法的操作是原子操作了么,那两个i++不就和i+=2是一个意思了么
@comparable:
兄弟你在说什么虎狼之词,这是语法,和原不原子操作没关系
i++ 和 i+=2 怎么可能一个意思
i++ 相当于 i = i + 1;
i+=2 相当于 i = i + 2;
建议找套基础教程,研究下Java语法,不要一上来就搞高级用法,基础真的很重要!!!
@飒沓流星: 你看清楚在回复好么
@comparable:
抱歉抱歉,是我先入为主了!我再研究下
@comparable:
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class AutomicityTest implements Runnable {
private int i = 0;
public synchronized int getValue() {
return i;
}
public synchronized void evenIncrement() {
// i += 2;
i++;
i++;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
evenIncrement();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
// AutomicityTest线程
AutomicityTest automicityTest = new AutomicityTest();
exec.execute(automicityTest);
// main线程
while (true) {
int value = automicityTest.getValue();
if (value % 2 != 0) {
System.out.println(value);
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
}
getValue() 方法 加上synchronized 就正常了
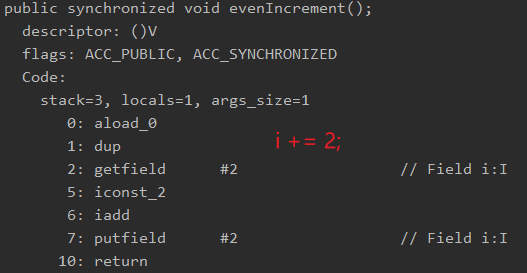
i += 2;
反编译后指令:
i ++;
i ++;
反编译后指令:
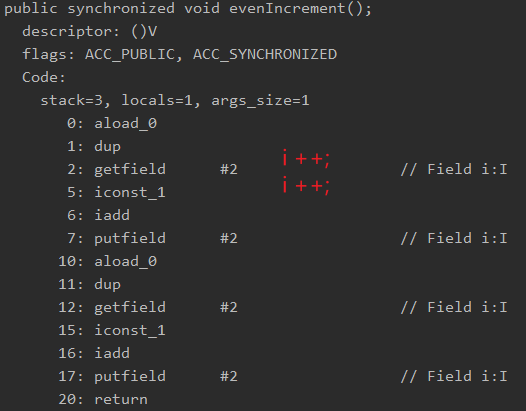
可以看到:
i++; i++;
字节码指令有两段putfield,由于之前getValue()没有加synchronized,那么在执行getValue()的时候,putfield可能没有执行,可能执行了一次,也可能执行了两次,没有执行是偶数,执行一次是奇数,执行两次是偶数;又因为线程run()是 while (true){}的,所以它总能执行到奇数,退出虚拟机。
i+=2;
字节码指令只有一段putfield,没有执行是偶数,执行了也是偶数,所以会死循环。
验证
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class AutomicityTest implements Runnable {
private int i = 0;
public int getValue() {
return i;
}
public synchronized void evenIncrement() {
// i += 2;
i++;
i++;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
evenIncrement();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService exec = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
// AutomicityTest线程
AutomicityTest automicityTest = new AutomicityTest();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(automicityTest);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(automicityTest);
Thread thread3 = new Thread(automicityTest);
Thread thread4 = new Thread(automicityTest);
Thread thread5 = new Thread(automicityTest);
Thread thread6 = new Thread(automicityTest);
Thread thread7 = new Thread(automicityTest);
Thread thread8 = new Thread(automicityTest);
Thread thread9 = new Thread(automicityTest);
Thread thread10 = new Thread(automicityTest);
exec.execute(thread1);
exec.execute(thread2);
exec.execute(thread3);
exec.execute(thread4);
exec.execute(thread5);
exec.execute(thread6);
exec.execute(thread7);
exec.execute(thread8);
exec.execute(thread9);
exec.execute(thread10);
// main线程
while (true) {
int value = automicityTest.getValue();
if (value % 2 != 0) {
System.out.println("main: " + value);
}
}
}
}
执行结果:
main: 5297
main: 8621
main: 9747
main: 10331
......
@飒沓流星: 好的,感谢。 反编译一下就很高大上










